The Role of 3D Printing in Automotive Manufacturing 
Additive manufacturing, sometimes known as 3D printing, has quickly changed a number of industries, including the automotive sector. In the pursuit of innovation, cost reduction, and efficiency, 3D printing has become a transformative tool for manufacturers. This investigation explores the many uses of 3D printing in the automotive manufacturing sector, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of this technology and how it can influence the direction of the sector going forward.
Understanding 3D Printing Technology
At its core, 3D printing is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This is achieved by laying down successive layers of material until the final object is formed. The technology can utilize a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites. Common methods of 3D printing include:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most common 3D printing technique, where thermoplastic filaments are heated and extruded layer by layer.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): In this process, a laser selectively fuses powdered material (often nylon or metal) to create solid structures.
- Stereolithography (SLA): This technique uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a layer-by-layer fashion.
Each method has its unique advantages and applications, making 3D printing versatile for various automotive manufacturing needs.
Applications in Automotive Manufacturing
- Prototyping and Design Validation
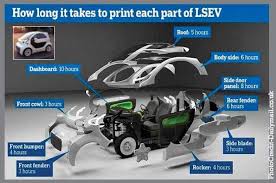
One of the primary applications of 3D printing in automotive manufacturing is rapid prototyping. Traditional prototyping methods can be time-consuming and costly, often requiring extensive tooling and setup. In contrast, 3D printing allows designers and engineers to quickly create physical models of components or systems, facilitating design validation and iteration.
- Speed: Prototypes can be produced in days rather than weeks, enabling faster feedback loops.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for expensive molds and tooling, making it financially viable to explore multiple design iterations.
- Complex Geometries: Designers can create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing techniques.
This rapid prototyping capability allows automotive manufacturers to innovate more efficiently, shortening the time from concept to production.
- Production of End-Use Parts

Beyond prototyping, 3D printing has advanced to the point where it can be used to manufacture end-use parts. This application is particularly relevant for components that are low in volume but high in complexity or customization needs.
- Customization: 3D printing allows for personalized components tailored to specific consumer preferences, such as custom interior fittings or unique design elements.
- Lightweight Components: The ability to create intricate designs enables manufacturers to produce lightweight parts, which can improve vehicle fuel efficiency and performance. For instance, 3D-printed lattice structures can replace heavier solid components.
- Low-Volume Production: 3D printing is ideal for producing small batches of specialized parts, such as replacement components for vintage or niche vehicles.
Cost Reduction and Supply Chain Efficiency
- Reducing Material Waste
Traditional subtractive manufacturing methods often result in significant material waste, as excess material is cut away to form the final product. In contrast, 3D printing adds material layer by layer, minimizing waste.
- Sustainable Practices: By reducing waste, 3D printing aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices, contributing to a lower environmental footprint.
- Streamlining Supply Chains
3D printing can significantly streamline supply chains by enabling localized production. Manufacturers can produce parts on-demand rather than relying on complex logistics networks.
- On-Demand Production: Parts can be printed as needed, reducing the need for large inventories and associated storage costs.
- Global Accessibility: With the capability to 3D print components anywhere, manufacturers can establish localized production facilities, reducing shipping times and costs.
Challenges of 3D Printing in Automotive Manufacturing
Despite its numerous advantages, the adoption of 3D printing in the automotive industry does face several challenges:
- Material Limitations
While 3D printing technologies have advanced significantly, the range of materials that can be effectively used for automotive applications is still limited compared to traditional manufacturing methods. High-performance materials required for critical automotive components often need more research and development to be viable for 3D printing.
- Quality Control and Certification

Ensuring the quality and reliability of 3D-printed components remains a significant challenge. Automotive parts must meet stringent safety and performance standards, necessitating rigorous testing and certification processes.
- Standardization: The lack of standardized testing methods for 3D-printed parts can hinder widespread adoption in safety-critical applications.
- Traceability: Ensuring traceability of materials and processes used in 3D printing is vital for compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Initial Investment Costs
While 3D printing can reduce costs in the long run, the initial investment in machinery, software, and training can be substantial. Smaller manufacturers may find it challenging to adopt this technology without significant capital expenditure.
Future Trends in 3D Printing in Automotive
- Advancements in Materials
The creation of novel materials appropriate for 3D printing in automotive applications is anticipated to advance research and expand the possibilities of the technology. Advances in high-performance polymers and metal 3D printing may create new production opportunities and allow for the creation of vital parts with increased robustness and longevity.
- Hybrid Manufacturing
The future of automotive manufacturing may see a blend of traditional and additive manufacturing techniques. Hybrid systems that combine subtractive and additive processes can enhance precision and efficiency, allowing manufacturers to leverage the strengths of both approaches.
- Integration of AI and Automation
Integrating artificial intelligence and automation into 3D printing processes will likely enhance efficiency and precision. AI can optimize design processes, predict maintenance needs, and streamline production workflows, making 3D printing an even more viable option for automotive manufacturers.
- Sustainability Initiatives
With growing awareness of environmental issues, the automotive industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability. 3D printing can play a crucial role in reducing the carbon footprint of manufacturing through waste reduction and localized production. As sustainability becomes a driving force in the industry, the adoption of 3D printing technologies will likely increase.
Case Studies
- Local Motors and the Strati
The Strati, a 3D-printed vehicle from Local Motors, garnered media attention. For the first time, this car was made almost entirely via additive manufacturing. Local Motors significantly shortened the time from design to final product by using 3D printing for the car’s body and other interior parts, demonstrating how swiftly and effectively a vehicle might be built.
- BMW’s Investment in 3D Printing
BMW has embraced 3D printing for various applications, including the production of customized parts and tools. The company uses 3D printing for producing components such as bracket supports and air intake manifolds. By integrating 3D printing into its manufacturing processes, BMW has reduced production times and improved the efficiency of its operations.
Conclusion
With its many benefits in terms of design flexibility, cost savings, and sustainability, 3D printing is revolutionizing the car manufacturing industry. Even though there are still obstacles to overcome, interest and investment in this technology are still fueled by its potential for efficiency and creativity. 3D printing will probably become more and more important as the automotive sector develops, enabling the production of cars that are not only more effective but also more sensitive to customer demands and environmental concerns.

Although 3D printing is still in its infancy, its influence on the automotive industry is already evident. Future prospects for the business and the customers who depend on these vehicles are bright as long as manufacturers keep researching and improving this technology. The combination of 3D printing and auto manufacturing signifies a cultural change toward a more creative, ecological, and adaptable automotive environment in addition to a technological advancement.
